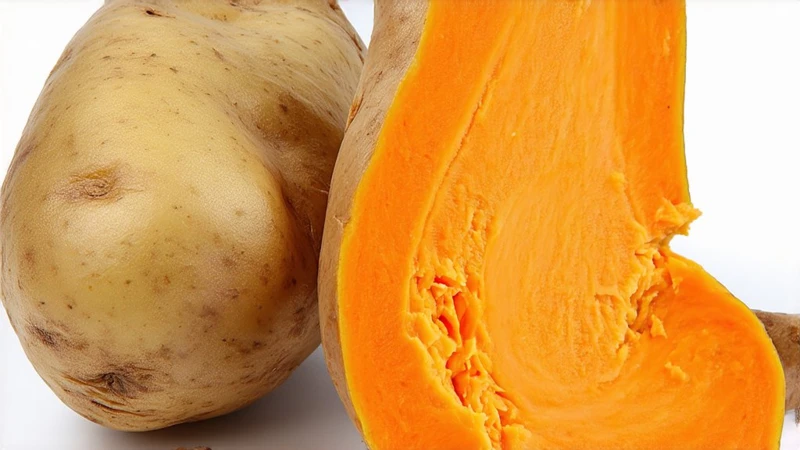
Jacket Potato vs Sweet Potato: The Ultimate Guide for Health Foodies
In a world where dietary choices are more often motivated by individual health goals or cultural trends and there are always more options, the debate over jacket potatoes (or baked potatoes, if you're in the United States) and sweet potatoes has never seemed more relevant. Each is nutrient-dense, versatile and beloved across cuisines, but their nutritional composition, flavor and culinary uses are different in ways that make them distinct. This article examines the battle of the spuds using scientific data, cultural insights and a dash of personal experience.
Decimal Perceptions: Data-Driven Comparisons
Let's start with the facts. Here's a table comparing key nutritional metrics for a medium-sized (114–130g) jacket potato and sweet potato using USDA data as a baseline:
Table 1: Macronutrient Comparison
| Metric | Jacket Potato | Sweet Potato |
|---|---|---|
| Calories | 130 kcal | 103 kcal |
| Carbohydrates | 26g | 24g |
| Dietary Fiber | 2g | 4g |
| Protein | 3g | 2g |
| Fat | 0.2g | 0.2g |
Table 2: Vitamins, minerals and glycemic index
| Metric | Jacket Potato | Sweet Potato |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | 0% DV | 438% DV |
| Vitamin C | 28% DV | 37% DV |
| Potassium | 620mg | 542mg |
| Glycemic Index (GI) | 78 (high) | 63 (medium) |
| Antioxidants | Low | High (beta-carotene) |
NOTE: DV = Daily Value based on a 2,000-calorie diet.
Calories & Macronutrients
Jacket potatoes win on protein (3g to 2g) but lose on fibre (2g to 4g). Sweet potatoes also offer similar carb counts, but their higher fiber and lower calorie content make them better for weight loss.
Vitamin A & C
Sweet potatoes reign supreme here, delivering more than 400% of the DV for vitamin A —essential for eye health —in the form of beta-carotene. Both are sources of vitamin C, but sweet potatoes again win out with 37% DV vs.28%.
Glycemic Index
With a GI of 78, jacket potatoes may raise blood sugar more than sweet potatoes (GI 63). This makes sweet potatoes a healthier option for diabetics, although consuming jacket potatoes with protein or fat can reduce the glycemic impact.
Taste & Texture: A Sensory Exploration
Sweetness & Flavor
Sweet potatoes do their name justice, containing 5–7% more natural sugars than jacket potatoes. Their earthy sweetness complements cinnamon or maple syrup, while jacket potatoes provide a starchy, neutral base perfect for savory toppings ranging from cheese to bacon.
Texture Differences
Jacket potatoes have a thick shaggy skin that becomes crisp when baked, unlike sweet potatoes, which have a thin, smooth skin. The flesh of jacket potatoes is fluffier, whereas sweet potatoes lean denser and moister, an attribute I've admired for dishes like roasted wedges.
Health Benefits: More Than a Good Thing
Blood Sugar Management
Being low GI with high fibre, sweet potatoes help control the glucose absorption and are thus, diabetes-friendly. Sweet potato extracts improved insulin sensitivity in a 2018 study in Nutrition & Metabolism that involved prediabetic individuals.
Heart Health
Both potatoes are rich in potassium (620mg vs. 542mg) which helps blood pressure need to be within limits. But the antioxidants in sweet potatoes may lower the oxidative stress associated with heart disease.
Digestive Health
Sweet potatoes encourage gut health, providing double the fiber found in jacket potatoes. One 2020 review in Nutrients found that fiber helps prevent colorectal cancer, giving sweet potatoes a leg up here.
Traditional Dishes
Jacket potatoes shine in American comfort classics like loaded baked potatoes slathered in sour cream and chives. Sweet potatoes, on the other hand, take center stage in Southern dishes like candied yams and pies from soul food.
Recipe Adaptability
The sweetness of sweet potatoes helps them straddle savory and sweet applications — from fries to muffins. Jacket potatoes are more stiffly savory but make for excellent vessels for substantive toppings.
Preparation Methods
BAKING: Both produce crispy skins, but sweet potatoes caramelize a bit, which amplifies their flavor.
Boiling: Sweet potatoes lose less nutrients as starch does not leak as much.
Fry: Use jacket potatoes for crispier fries, or choose sweet potatoes for a healthy, nutrient-dense option.
People like you: Who watches what?
Dietary Restrictions
Sweet potatoes are also gluten-free, vegan staples, whereas jacket potatoes need ingredient choices (like vegan cheese) to be considerate of these dietary needs.
Cultural Trends
Sweet potato consumption in the United States has soared by 18 percent over the past decade as wellness trends have taken hold. Jacket potatoes, meanwhile, are a nostalgic comfort in Midwest diners and family dinners.
Bible and Personal Reflection
Scripture tells us, "So whether you eat or drink or whatever you do, do it all for the glory of God" (1 Corinthians 10:31). When cooked mindfully, both potatoes embody this principle. I tend to prefer sweet potatoes for their antioxidant power, however, I always have jacket potatoes in stock for warm, decadent dinners.
Conclusion: Who is the Real Best?
The verdict? It's up to what matters most to you:
Sweet potatoes are all about vitamin A, fiber, and blood sugar regulation.
Choose jacket potatoes if you want a blank canvas to add toppings to or need a protein hit.
Ultimately, both deserve a place in a well-rounded diet. Like everything, moderation and intentionality matter — whether you're roasting, baking or braising them.
What's your spud of choice? Share your thoughts below!
Data Sources: USDA FoodData Central, Nutrition & Metabolism (2018), Nutrients (2020)